NALM6 Chemogenomics Screens
We will screen the compound(s) of your choise and we will provide you with the results. For academic and
non-profit screenings, please understand that the findings will be made publicly available on our platform three
years after the results are delivered. In contrast, data from industry screenings will be kept confidential.
Academia: $2,600 CAD per compound
Industry: please contact for a quote
The Basics
The main service offered by ChemoGenix is screening genome-wide pooled CRISPR/Cas9 KO in the NALM6 cell line
grown in the presence of compounds affecting cell growth. If your compound possesses the ability to interfere with
NALM6 cells proliferation (we test that prior to screening), we can identify all genes related to the specific
activity/pathway responsible for the growth inhibition.
Our screens test in a single experiment every gene KO ability to increase either sensitivity (synthetic lethality)
or resistance (rescue) to compound-induced growth inhibition. The resulting genetic signature provides the
rationale to confirm or discover the compound mechanism of action (MOA), identify novel gene functions associated
with the specific chemical perturbation or even uncover unexpected secondary effects.
The Screens
Our screens exploit a NALM6 clone that inducibly controls the expression of Cas9 with doxycycline. The clone
has been infected with lentiviruses encoding the sgRNA EKO library (>278K sgRNAs targeting the human genome at
10 sgRNA per gene) at a low multiplicity of infection (MOI), followed with blasticidin selection, to deliver a
single sgRNA per cell (PMID:29038160). Because Cas9 is not constitutionally expressed we could N2-freeze the
library without depletion of sgRNAs targeting essential genes. Anytime we perform a new screen, we simply recover
a new aliquot for 1 day in media (minimum pooled representation of 250 cells per sgRNA), induce knockouts and
expand the pool for 7 days in media with 2 ug/mL doxycycline. Cells are then separated in T-75 bottles, 70 mL
of cells at 4E5 cell per mL (28E6 total, representation of 100 cells per sgRNA) and each of them treated with a
specific compound, mostly aiming at achieving 50% growth inhibition. Every two days, growth is monitored via
cell counting and, whenever cell concentration exceeds 8E5 cells per mL, cells are diluted back to 4E5 cells
per mL and supplied with a compound/drug to maintain dosage. After a total of 8 days of outgrowth in presence
of the chemicals, cells are pelleted, genomic DNA extracted and sgRNA sequences amplified by PCR. NGS of sgRNA
sequences is done on an Illumina NextSeq 2000. sgRNA frequencies are then used to compute
statistically robust gene scores.
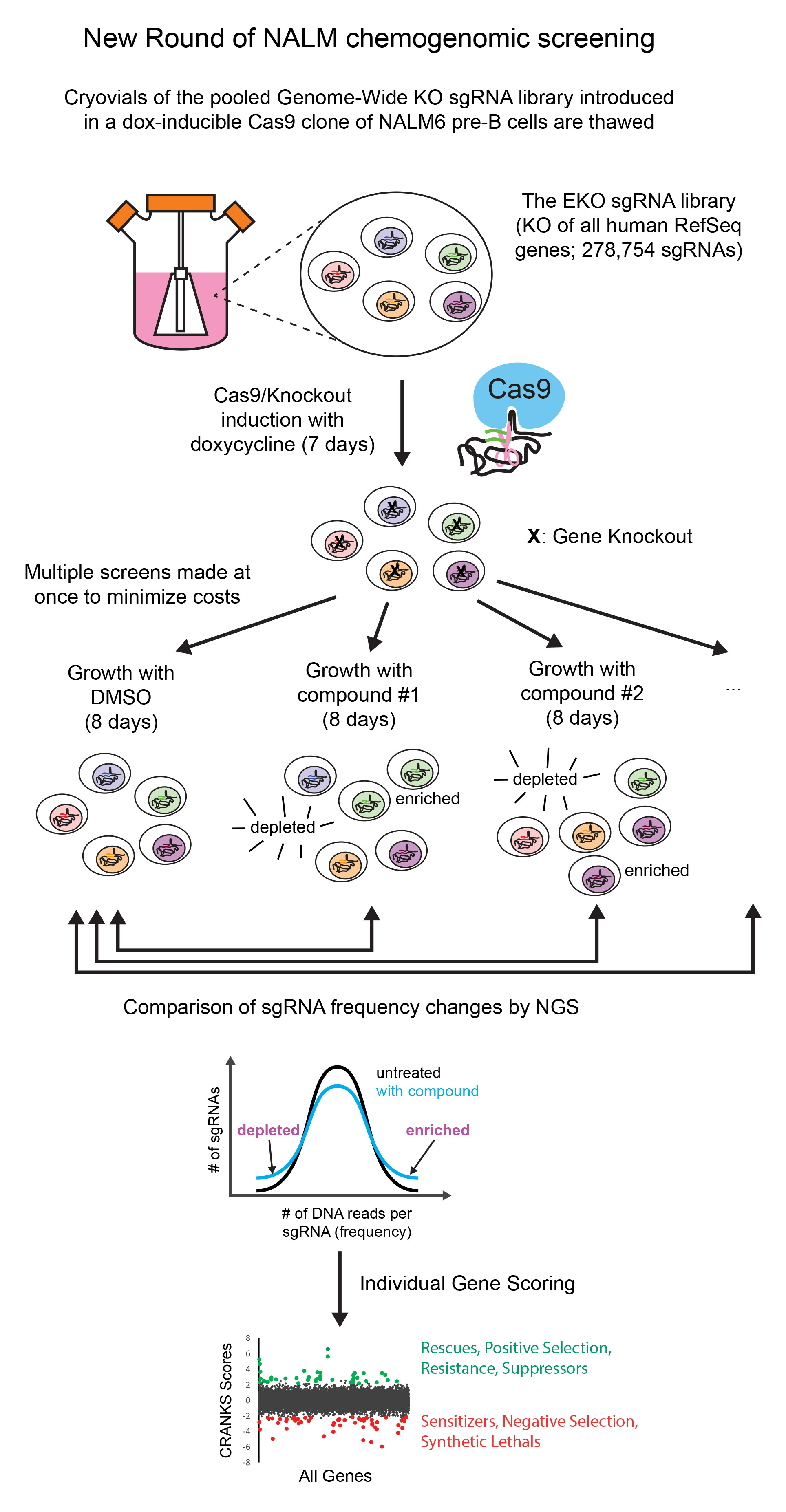
Regarding the Dose Effect
Dosage of compounds is a crucial variable in chemogenomics experiments. Whenever a tested compound displays
more than one activity, the screen will provide a signature related to the cellular process that has the
largest influence on growth, which may or may not be the expected one. Furthermore, a high dose usually triggers
a higher magnitude of growth inhibition, favoring mostly rescues (suppressors of genetic interactions) while a
low dose, inducing little growth inhibition, favors synthetic lethals (enhancers of genetic interactions). As
a default, we suggest to screen at a dose inducing about 50% of growth inhibition. In our 8-day screens we aim
at a dose capable of generating 3.75 population doublings, compared to 7.5 population doublings in untreated cells.
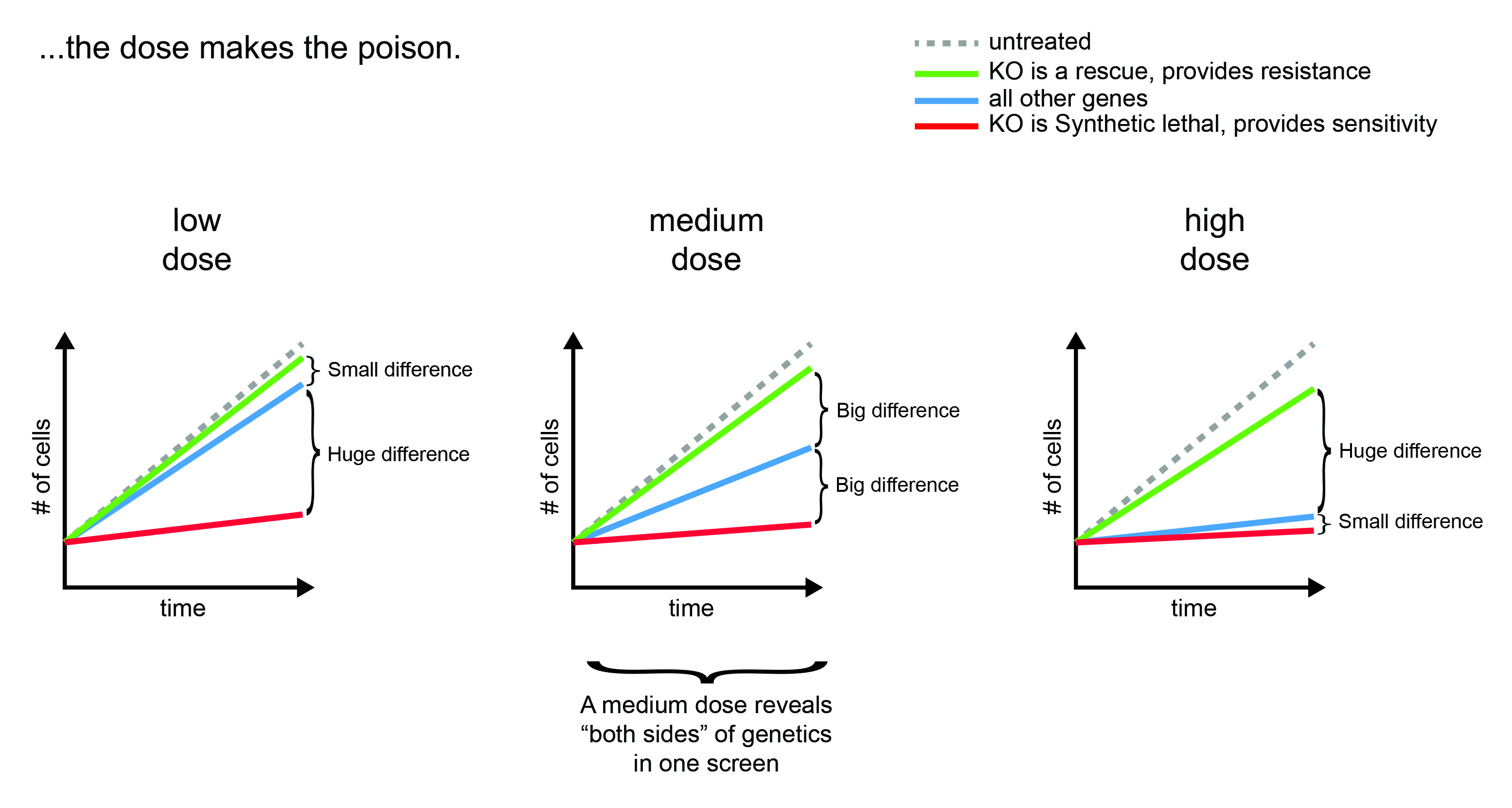
We usually recommend screening at an adequate “middle dose” to gather information on both the resistance and sensitivity mechanisms rather than just one of the two. However, screening the same compound both at low and high dose would likely yield more hits and therefore be more informative than a single “middle dose” screen. That said, we will screen at any dose you may choose.
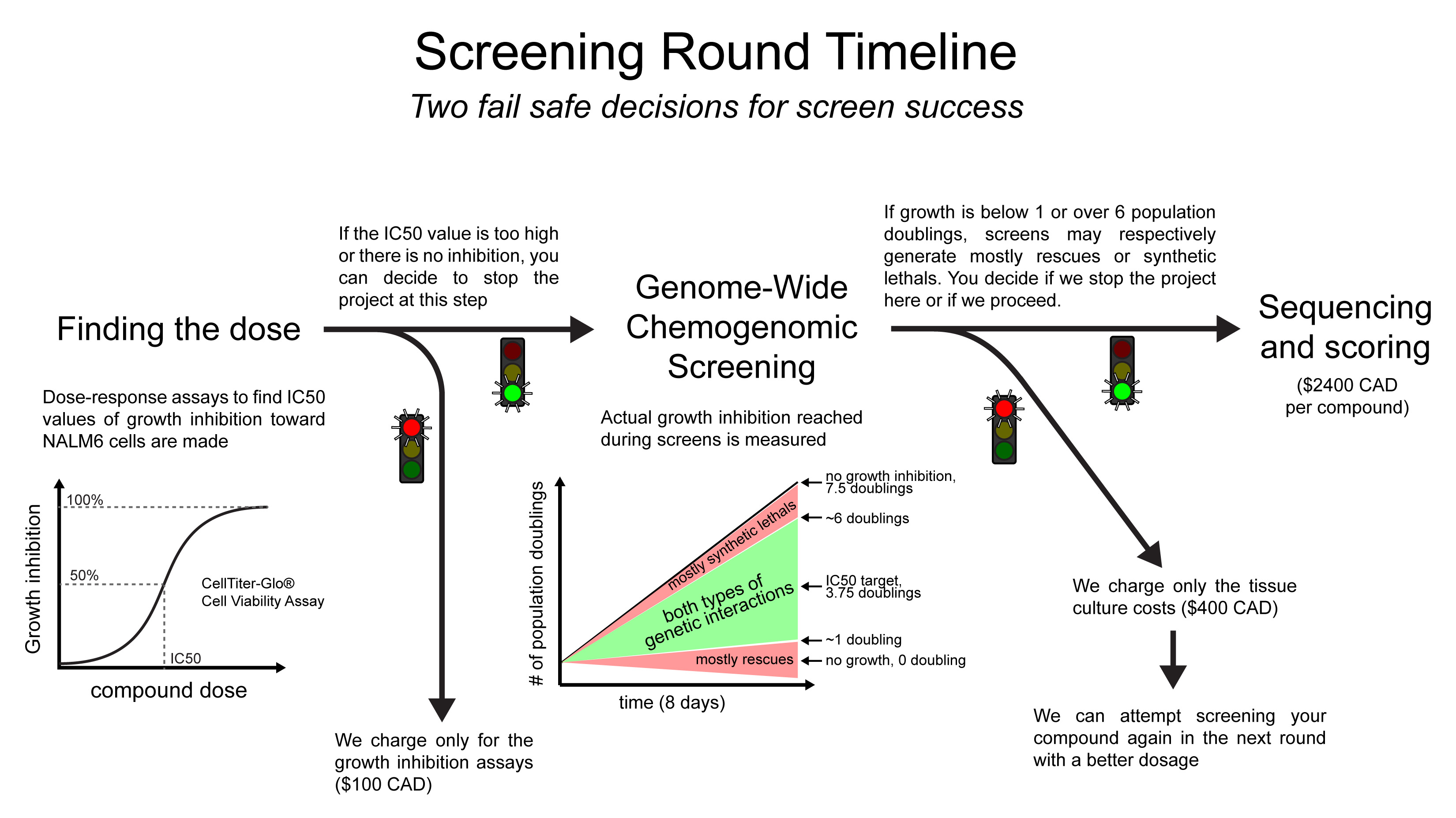
Timeline and Go/No-Go Decisions
In order to optimize costs and operations, ChemoGenix operates in “rounds” of screens, meaning that each round
is launched once we have received a minimal number of compounds, on average every 4 months. First, we test
your compound activity with a dose-response assay to determine what dosage affects the proliferation of NALM6
cells. Once we identify the concentration causing 50% of NALM6 growth inhibition, we will contact you if this
concentration is above a specific threshold set by you. This step is crucial because you may know at what dosage
this compound acts on its target and you may also know that screening at such a high concentration may actually
just reveal a secondary mechanism that you are not interested in. At this step, you will decide whether or not
we should proceed with the screen at the expected IC50 dose. If the compound does not inhibit growth, perhaps
there is no point in moving forward with the experiments. As an aside note, we had some success (identification
of synthetic lethal hits) screening a handful of compounds that didn’t display any cytotoxic activity.
Because many factors can influence the actual growth inhibition during screening conditions (culture volumes, compound stability, steep dose-response curves), we carefully monitor cell growth over the course of the experiment. Usually, most screens generating between 1 and 6 population doublings provide meaningful genetic information, and we recommend their sequencing. Outside this window, it is a gray area. Sometimes the screens provide meaningful genetic information: mostly rescues or mostly synthetic lethals. Other times, it just generates noise and we cannot predict which one we will have until we commit to costly sequencing and analysis. At this juncture, you must determine whether to continue with the sequencing and data analysis or to halt the experiment and consider testing with an alternative dosage in the subsequent round. Should you opt not to advance with the experiment, you will incur only the expense associated with the screening, which amounts to $500 CAD. It is important to recognize that evaluating the same compound at varying dosages can yield a deeper insight into the genetic factors associated with its activity. Consequently, you may derive greater benefit from conducting a high or low dose screening, followed by a re-evaluation of the same compound at a mid-range dosage later on.
Data Confidentiality
The findings from academic and non-profit clients will be made publicly accessible on this website three years
after their completion. If you prefer to keep this data confidential beyond that period, we are willing to collaborate
with you to secure sponsorship and funding for an alternative screening involving a compound of our choice, which will
be promptly released to the public. However, this provision does not extend to for-profit clients, who retain exclusive
ownership of their data.
Contact us
Please contact us in order to discuss your needs and to
take advantage of the most appropriate solution.